rigid flex circuits
Rigid flex circuits (also known as rigid-flex) combine the component and routing density of rigid boards with the flexibility of flexible circuitry in one package. This unique packaging method is used in products like laptop computers, smartphones and tablet computers, wearable electronics and more. Rigid flex is typically used in applications that require a high degree of reliability and durability, but where space constraints and/or complexities are limiting factors.
The rigid flex circuits design is based on a combination of rigid and flexible substrates that are laminated together to create rigid and flex areas in the same construction. The conductor layers of the rigid and flexible sections are connected to each other through plated holes. The rigid section of the board is constructed with an epoxy or acrylic adhesive, while a low-flow prepreg may be used in the flexible area to support the copper foil. Copper is added either by lamination to the adhesive or chemical plating on top of a seed layer.
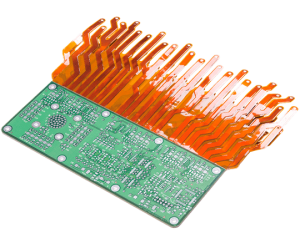
A rigid-flex PCB can be made using both single-sided or double-sided plated through hole (through-hole) technology. Typical single-sided flex circuits consist of a layer of solder mask on one side and an insulating dielectric film on the other. The insulating dielectric is then pre-etched, creating the pads on which components are mounted. A pattern of etched copper is then exposed through the resist on the flex circuit. The etching process is completed, and the flex circuit is then bonded to the rigid section of the board using an adhesive.
What are rigid flex circuits?
The bonded rigid-flex circuits are then cut and v-scored to create break-away tabs for assembly into the final product. The v-scoring and tab removal are performed to allow for easier handling of the circuit during the “pick and place” and wave soldering processes. The flex circuits are then blanked into a final assembly panel that includes borders for framing. This helps to ensure that the flex sections of the rigid-flex remain flat during final assembly in the reflow oven.
When used correctly, rigid flex circuits offer designers the freedom to use more complex and compact electronic packaging. They also provide greater dynamic and mechanical stability, reduced points of failure during drop testing and improved performance when the product is subjected to shocks or vibrations.
In addition to these advantages, rigid-flex circuits can be cost-effective when compared to traditional rigid PCBs. This is due to the fact that they can often reduce the number of components and connectors needed for a given application. This can lead to lower material and assembly costs.
As with any printed circuit board, it’s important to work with experienced engineers and PCB manufacturing designers to help with the rigid flex design and fabrication process. This collaboration can ensure that your rigid-flex circuits are designed, fabricated, and assembled to meet all of the application requirements. Additionally, it’s critical to conduct thorough testing and verification processes to make sure that your rigid-flex PCB meets all the required specifications.